Analysis of electrical resistivity of cable insulation
Electrical properties refer to surface resistivity and volume resistivity, dielectric constant, dielectric strength, and dielectric loss tangent, as they are the most important properties for determining whether a material is suitable as an insulating material.
Electrical properties can be divided into two groups. In general, the first group evaluated the ability of the polymer to resist low-intensity electric fields, including properties such as dielectric constant and dielectric loss tangent. The second group is an important property required in high-intensity electric fields, such as discharge and breakdown. The dielectric strength of an insulating material can be defined as the maximum voltage required to produce a dielectric breakdown, expressed as the value of the dielectric breakdown voltage divided by the thickness of the material.
The tendency to aggregate will result in a larger volume within the pores. These pores will promote current leakage, causing the device to be subjected to discharge, so that the polymer compound is rapidly broken down. The data also shows that this performance is slightly better if the compound contains untreated ATH because the treatment will impart an inductive polarity to the filler.
Resistivity is a measure of the resistance of a material to the flow of its surface or its volume. In order to avoid leakage, the value of the resistivity must be as large as possible. The compound has a minimum resistance value which is close to the resistance value of the pure rubber as the amount of N330 carbon black is reduced.
It can also be observed that the silane treatment process does not have any significant effect on the resistance value. After surface treatment, the bond between the masterbatch and the filler is better and has a positive effect. However, this positive effect is likely to be offset by the presence of polar groups in the coupling agent, resulting in a decrease in the volume resistivity. The change in surface resistivity is related to factors such as impurities and humidity.
Slim Rotary Damper mainly used for small diameter, long height space. Shaft Damper is used to dampen drives, control speed, and many other applications. Shaft damper are widely used in invisible screens. Shaft damper can make the movement of structures soft, quiet and safe to mitigate the impact, avoid the damage, increase the mechanical life, reduce noise, and improve product quality.
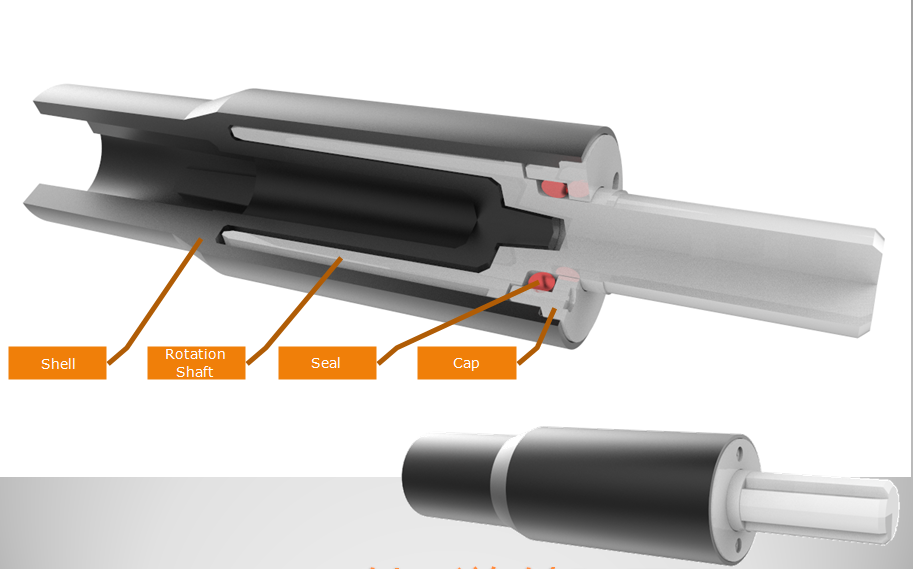
NOTE:
1. Please contact the corresponding product engineer for specific torque products
2. Max. rotation speed: 50r/min
3. Max. circle rate: 5 cycle/min(Clockwise180 °, 180 ° anti-clockwise for 1 cycle)
4. Operating temperature: -10~50℃
5. Storage temperature:-30~80℃
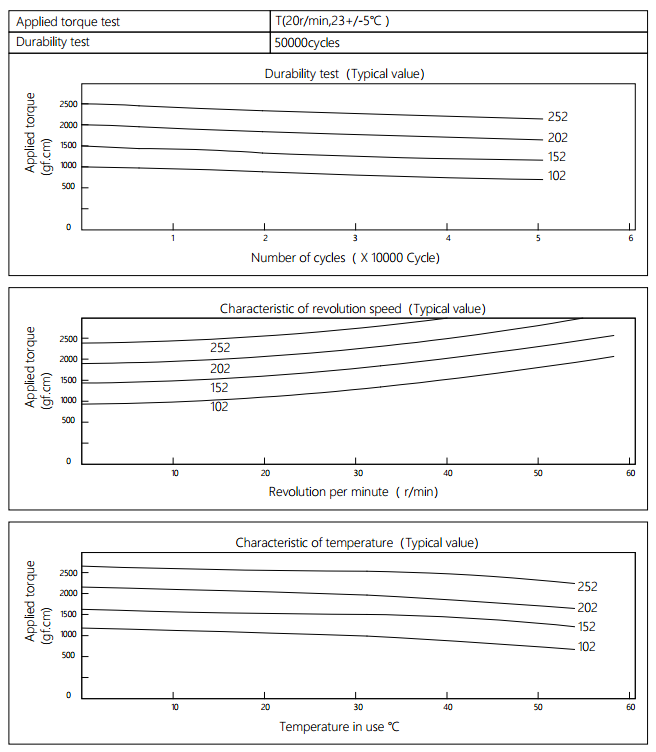
Applied torque: (T)
Test Temperature: 23+/-5℃
Rotating speed:20r/min
Durability test Method:Clockwise 180 °, 180 ° anti-clockwise
Rotating speed: 20r/min
Test Frequency: 1cycle/min
Test Temperature: 23±5℃
Durability test cycle: 50000cycle
Test result criteria: Store in the room temperature for 24 hours or more after the test, recording to the torque T=T±30%T.
Shaft Damper
Shaft Damper,Drive Shaft Damper,Crankshaft Damper,Flexible Shaft Coupling
Shenzhen ABD Equipment Co., Ltd. , http://www.abddamper.com