Progress in in-situ monitoring of low-cost phosphorus forms in lakes and their geochemical characteristics
China Instrument Network Instrument Development Phosphorus is widely recognized as a limiting nutrient that significantly influences water productivity and can trigger excessive algal growth. Understanding the complex interactions between phosphorus biogeochemistry and ecosystem responses is crucial for improving water quality and restoring ecological balance. Most existing studies focus on oxidized phosphorus species, such as pentavalent phosphate, while neglecting the presence of more reduced forms like trivalent or monovalent phosphorus, as well as the less commonly studied negative trivalent phosphorus. Recent research has increasingly shown that these low-cost phosphorus forms are widespread in natural environments, and their redox processes may play a more critical role in maintaining overall ecosystem stability and elemental cycles than previously thought.
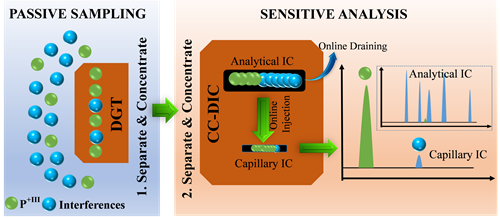
In-situ analysis technical process of low-cost phosphorus in the environment
The frequent occurrence of eutrophication in Chinese lakes often leads to large-scale hypoxia, which significantly alters the form and environmental behavior of phosphorus. However, due to the low concentration, instability, and high susceptibility to interference of these low-cost phosphorus species, traditional analytical methods struggle to accurately characterize them. This limitation has hindered our understanding of phosphorus dynamics, including its migration and transformation in eutrophic lake systems.
Recently, researchers from the Nanjing Institute of Geography and Lakes, Chinese Academy of Sciences, led by Han Chao, have pioneered an innovative approach by combining in-situ sampling with advanced two-dimensional capillary trace analysis techniques. This method enables the simultaneous separation and online monitoring of various phosphorus species in complex environmental matrices. It allows for real-time purification and enrichment of ultra-trace phosphorus, significantly enhancing detection sensitivity and enabling precise reconstruction of low-cost phosphorus information in natural settings. Using Lake Taihu as a case study, the team conducted both laboratory simulations and field monitoring experiments to investigate the distribution patterns and controlling mechanisms of low-cost phosphorus at the sediment-water interface in anoxic zones.
These findings were published in *Water Research* under the title "In situ sampling and speciation method for measuring dissolved phosphite at ultratrace concentrations in the natural environment." The study was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China, the Natural Science Foundation of Jiangsu Province, and the National Key Laboratory of Pollution Control and Resource Research.
(Original title: In-situ monitoring of low-temperature phosphorus forms in lakes and research on their geochemical characteristics)
Outdoor Repair Supplies,Waterproof Repair Kit,Field Repair Kit,Outdoor Research Repair Kit
KRONYO United Co., Ltd. , https://www.kronyotirerepairkit.com